Archive
Semicon to grow 4-8pc in 2008; ASPs trending up
It has really been a tumultuous year for semiconductors, which has held up very well, despite the memory market turmoils, so far.
 Just a day ago, Future Horizons reported on the June sales for semiconductors. According to Malcolm Penn, chairman and CEO, June’s WSTS results brought both good and bad news! The good news being that the recovery momentum strengthened, with Q2 sales up 3 percent on Q1.
Just a day ago, Future Horizons reported on the June sales for semiconductors. According to Malcolm Penn, chairman and CEO, June’s WSTS results brought both good and bad news! The good news being that the recovery momentum strengthened, with Q2 sales up 3 percent on Q1.
He says, “This was significantly better than even we dared to predict in last month’s Report, despite the fact we raised eyebrows and disbelief by suggesting a 2.3 percent quarter on quarter growth.”
The bad news was the Jan-May YTD WSTS numbers for standard logic (and thus, the total ICs and total SC) were revised downwards by a sizeable US$1.4 billion, a restatement that will knock 2 percentage points off the 2008 year on year growth number!
What were the reasons for the recovery momentum to have strengthened, with Q2 sales up 3 percent on Q1? Penn adds: “The first half year sales were much stronger than everyone (except us) believed. It has depresses, only by memories.”
Also, the Jan-May YTD WSTS numbers for standard logic (and total ICs and total SC) were revised downward by a sizeable US$1.4 billion. Why did this happen? It is interesting to note that one company mis-reported its sales for Jan-May and corrected this reporting error in June.
Penn adds: “This often happens, but not before at this magnitude. Individual company details are secret, so we do not know who the culprit was or how the ‘error’ happened.”
Forecast revised to 4-8 percent
Future Horizons further says in its report that the downward revision in standard logic numbers would knock 2 percentage points off the 2008 year on year growth number. On quizzing, Penn agrees: “Yes, our ‘revised’ forecast range is 4-8 percent. We are currently still erring on the high side of this range. More important though is the market momentum.”
Memory has been a constant problem this year. iSuppli has mentioned in an earlier report that NAND recovery will be likely in H2-2009.
DRAMeXchange, in another report today, indicates a new record low for DDR 1Gb. Even Penn agrees that recovery is definitely not in sight. When do we actually get to see some recovery? He adds: “There is still over capacity, however, Q3 is typically the strongest demand quarter.”
Still on memory, does Future Horizons forsee Hynix bouncing back? Penn says: “They did; in 2000-02, they were on the verge of bankruptcy. Now, they are fitter and financially strong.”
ASPs were trending up earlier, and the status quo is maintained. “ASPs are still trending up, slowly, but surely. We will be commenting more on this in September’s report,” he adds.
Fab spends trending down
Just a few days ago, a SEMI analyst highlighted the chief reasons for decline in fab spends. Christian Gregor Dieseldorff, Senior Manager of Fab Information and Analysis at SEMI, said: “Given the weaker economic conditions globally, coupled with higher energy and commodity prices and the financial crisis, the overall outlook for semiconductor growth in 2008 is for low-single digit growth in both revenues and units. As such, device makers have responded by cutting back their capital spending and pushing out fab projects or putting them on hold.”
On the status with fab spends, Penn agrees, “Those are still trending down, and will continue to do so for at least the next three quarters.”
Solar not much help
There have been lot of investments happening in solar/PV. One may imagine that all of this would be helping the global semiconductor industry. So, is the spend in solar/PV really helping the industry? Penn disagrees, saying this only helps the equipment guys.
One last query, and this is regarding the smaller IDMs, ‘fab-lite’ IDMs, and fabless semiconductor companies. Are they growing at below average? Penn concludes: “They are mostly not. The fabless firms outgrew the market 2x in the first half of 2008.”
Perhaps, here also lies a message for India!! One hopes that India does not get too carried away by all those investments in solar/PV, and focuses more on the semicon side. Semicon in India, does need concrete planning, after all!
90pc fab investments for 300mm capacity: SEMI
Recently, SEMI (Semiconductor Equipment and Materials International) released its World Fab Forecast report. This report mentions that projected decline in world semiconductor fab equipment spending of 20 percent is likely for 2008. However, a rebound of over 20 percent in spending is expected in 2009, driven by over 70 fab projects.
The August 2008 edition of this report lists 53 fab equipping projects and up to 21 construction projects for fabs in 2009. It is sincerely hoped that at least one of the fabs likely from the Southeast Asian region is from India!
With the help of Scott Smith Senior Manager, Public Relations, SEMI, I was able to get in touch with Christian Gregor Dieseldorff, Senior Manager of Fab Information and Analysis at SEMI, in an attempt to find out more about the decline in global fab spends, these new fabs, and how these fabs can lead a turnaround in the global semiconductor industry. Thanks Scott!
 So what are the chief reasons for the decline in fab spends during 2008? According to Dieseldorff, given the weaker economic conditions globally, coupled with higher energy and commodity prices and the financial crisis, the overall outlook for semiconductor growth in 2008 is for low-single digit growth in both revenues and units. As such, device makers have responded by cutting back their capital spending and pushing out fab projects or putting them on hold.
So what are the chief reasons for the decline in fab spends during 2008? According to Dieseldorff, given the weaker economic conditions globally, coupled with higher energy and commodity prices and the financial crisis, the overall outlook for semiconductor growth in 2008 is for low-single digit growth in both revenues and units. As such, device makers have responded by cutting back their capital spending and pushing out fab projects or putting them on hold.
I was keen to find out the geographic breakup of these 70 new fabs that are likely yo come up in 2009.
Dieseldorff advised that these are not 70 new fabs coming up in 2009. Rather, the numbers reflect 300mm fabs only, and is a mix of on-going and new projects for fabs equipping and fab construction projects in 2009.
For equipping 300mm fabs, SEMI expects about: Americas 8, China 5, Europe and Mideast 4, Japan 7, South Korea 11, SE Asia 3 and Taiwan 15.
For 300mm fab construction projects, SEMI expects about: Americas 3, China 2, Europe and Mideast 1, Japan 2, South Korea 3, SE Asia 2 and Taiwan 8.
What are the salient features of some of these new fabs likely to come up next year (for instance, new tech nodes)? Dieseldorff highlighted that about 90 percent of the investments are for 300mm capacity, and the amount of spending for advanced nodes, such as 65nm, is increasing.
“Also, device makers are building larger fabs, which are termed “mega fabs,” so, to potentially realize a greater return based on scales of economy,” he added.
How will these new fabs contribute to a better performance from the global semicon industry? This will be quite interesting to witness.
Dieseldorff said that over the past several years, demand for semiconductor devices has been quite strong, and so, the industry has had to bring on capacity to support this need, both in terms of needed capacity and technology. Even with the slower market growth in 2008, recent industry data shows healthy levels of fab capacity utilization, especially for the advanced technology generations and for 300mm manufacturing.
He added: “The expectation is that demand for semiconductors will strengthen once global economic conditions improve. So, the capacity addition that is coming online this year and the fab projects that are equipping and beginning construction in 2009 are necessary to meet the future demand.”
So how will all of this affect the overall memory market (e.g., 42pc increase in share for memory)? Dieseldorff shared his thought, a fact, known well to those in the semiconductor industry, that the memory market has been battered by declining average selling prices and a condition termed by some as “profitless prosperity.”
“Looking at demand forecasts specific to memory, tremendous growth is anticipated,” he forecasted.
However, the manufacturers in this device segment are battling it out for market share, and the general expectation is that consolidation will continue.
Also, joint-ventures and partnerships are becoming increasingly critical in the memory sector as manufacturers seek to leverage their existing resources to meet future technology and capacity requirements.
It would be interesting to find out why Taiwan and Korea are forecasted as likely to exceed Japan in fab spend?
According to Dieseldorff, in Korea, Samsung has been and is the key spender, and as a company, it will continue to invest so to have a dominant share in the memory sector.
He said: “In 2009, our expectation is for the DRAM manufacturers in Taiwan to boost spending after cutting back this year. We expect seven new 300 mm fab lines in Taiwan to come into production over the next two years.”
However, spending in Japan has been more measured and is likely to remain so. Toshiba, and its joint-venture partner, Sandisk are the big spenders in Japan, when it comes to new fab capacity. Other Japanese semiconductor manufacturers are more cautious and are focused more on technology spending.
IC shipments likely to grow 3.8pc in 2008
The latest wireless/DSP bulletin from Forward Concepts has highlighted an improved shipments of DSP and RISC chips for cell phones as well as DSP shipments for wireless infrastructure.
I had the privilege of interacting directly with Will Strauss, President & Principal Analyst, Forward Concepts, author of this particular bulletin.
On being quizzed about the improvement in shipments of DSP and RISC chips for cell phones, Strauss indicated that new cellular subscribers in China and India are continuing to grow, even as Europe and the US are reaching saturation.
“Since most people here have cell phones, the market is mostly driven by the replacement devices. In the US, handsets are also subsidized by the carriers under a subscription plan that ties the subscriber to a handset for two years,” he says.
An interesting point in the wireless/DSP bulletin is the fact that although DSP shipments for wireless infrastructure were down 14 percent in May compared to April, it was still 30 percent higher than May of 2007. What are the reasons for this peculiar trend?
Citing that the reasons were not yet clear, Strauss adds that in infrastructure, more so than for cellphones, the quarterly shipments are all that really matter. Forward Concepts hopes to have better calibration when June shipments are reported at the end of July.
Going forward, how are DSPs likely to perform? Well, it is to be noted that DSP chips, as devices with that specific nomenclature, are now becoming a decreasing percentage of the DSP silicon market. That’s because DSPs as cores are becoming just part of SoCs in everything multimedia, in VoIP, in cell phones, etc., adds Strauss.
Similarly, RISCs, like DSPs, are simply part of the SoCs, and often in lock step with DSP. That’s because every cell phone chip has at least one DSP core and one RISC core inside.
Another point noticeable in the bulletin is that automotive, wired communications and storage (disk drive controllers) sectors have seen a slowdown.
On this, Strauss clarifies that the automotive market has seen a drastic slowdown because of high fuel prices. Telecom companies have been slow to invest in infrastructure as wireless is taking over their traditional wireline market.
As for the disk drive controllers, their prices are akin to those of DRAM memory, subject to big swings in selling prices, lowering revenue even when production is strong.
Mobile Internet devices or MIDs are devices people are looking forward to. It is hoped they would bring some cheer to the IC market. This remains to be seen as the MID market doesn’t begin until late in Q3 2008.
Finally, the key question: what’s the industry outlook likely to be for the rest of the year? Strauss says: “The semiconductor industry is also subject to world economic changes. The outlook is for minimal world economic growth in 2008, mostly because of high oil prices and the weak US dollar. We are forecasting only 3.8 percent revenue growth in worldwide IC shipments for 2008, down from its traditional annual growth rate of about 7 percent.”
Collision course ahead?
On another note, the IC Insights reported that current spending plans by IC manufacturers worldwide will lower total semiconductor capital expenditures by 18 percent to $49.7 billion in 2008 from $60.3 billion in 2007, according to new data collected by IC Insights.
A growing number of large IC firms are now outsourcing more products to foundries. Also, major pure-play wafer foundries are aiming to increase their profitability by controlling capital spending. As such, IC Insights believes that the IC industry continues on a “collision course” with respect to supply, demand, and average selling prices or ASPs!
Semicon is no longer business as usual!
The Global Semiconductor Monthly Report June 2008 from Future Horizons, states: Let the market beware; it is no longer business as usual!
I would completely agree! For instance, the industry has since long moved to fabless, and now, fabless firms are ranking among the very best. Or, even from 130nm to 22nm process nodes, or from 180mm fabs to 450mm fabs!! Fair enough?
Coming back to the industry trends, Malcom Penn, CEO, Future Horizons, says that compared with March, the IC units were up and ASPs were down in April, even after adjusting for March being a five-week month. The net result was a 7.7 percent revenue decline! Does this spell more bad news for the beleaguered chip market?
Certainly, this seems to be the industry consensus view. Always the contrarian, Future Horizons’ views are different. Here’s how! April’s results came in exactly as expected. Also, the unit rise and fall was simply the result of the engrained ‘making the quarterly number’ mentality!
Digging beneath the layers reveals a set of market fundamentals that are in remarkably strong form. The penny may not yet have dropped to the table, but, even for the chip industry ever full of surprises, let the market beware; it is no longer business as usual.
Penn says: To paraphrase the late Sir Winston Churchill’s comments on Russia, “The chip industry too is a riddle wrapped up in an enigma”. It marches to its own complex interwoven pattern of rules, each relatively simple when viewed in isolation, but contriving to interact in a volatile and unique way. Right now, the industry is at its most confused [state] for a decade, battered by a barrage of uncertainties and contradictions. Shell-shocked and confused, confidence is off the agenda … just when what is needed most is cool heads and determination.”
Be it falling cap ex, tight capacity, focus on profits, continuing strong market demand, second half seasonal effects, according to him, the forecast tea leaves all seem to be pointing in the same positive direction. Has the worm finally turned then for the industry? He thinks so! Future Horizons also thinks that the “penny has yet to drop and that the impact on the market will be seismic and dramatic”.
Earlier, the Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA) reported that worldwide sales of semiconductors of $21.8 billion in May were 7.5 percent higher than the $20.3 billion reported for May 2007, reflecting continued strong sales of consumer electronic products. May sales were 2.8 percent higher than the $21.2 billion reported for April 2008.
Do bear in mind that May is historically a strong month for semiconductor sales, as per SIA.
NAND strong minus Apple effect
DRAMeXchange has indicated in its monthly review on the DRAM segment that the NAND Flash prices are likely to gradually stabilize after mid-July pushing by lower price, new demand from 3G iPhone, smart phones and low-cost PCs.
Elsewhere, as reported by Semiconductor International, according to Semico, NAND unit shipments are likely to cross over 3.5 billion units in 2008 as against 2.5 billion units in 2007, leading to a year-over-year growth of 35 percent.
However, reflecting the memory segment’s ASP (average selling price) crunch, NAND revenues will grow 13 percent in 2008, down compared to 25 percent in 2007.” Semico has said that the NAND industry will record a growth year in 2008, without experiencing what it has called the ‘Apple effect’.
Heartening solar initiatives
The one heartening thing to note has been the various solar related initiatives that have taken place over the past month (actually, for over the year!). In fact, iSuppli has probably been spot on while analyzing that investments in solar and semiconductors could be on par by 2010!
SVTC Technologies, an independent semiconductor process-development foundry, announced that its SVTC Solar business unit has launched the Silicon Valley Photovoltaic Development Center in San Jose. Canadian Solar and LDK Solar signing a new agreement for an additional 800MW of solar wafers, besides LDK updating on its polysilicon plant in China.
National Semiconductors also entered the PV market with its SolarMagic technology that maximizes solar energy production. Evergreen Solar, a maker of solar power panels with its proprietary, low-cost String Ribbon wafer technology, signed two new long-term sales contracts. Tokyo Ohka Kogyo Co. Ltd and IBM are also collaborating to establish new, low-cost methods for developing the next generation of solar energy products.
Not be left behind, Intel too is spinning off key assets of a start-up business effort inside Intel’s New Business Initiatives group to form an independent firm called SpectraWatt.
In India, solar has been making rapid strides, especially at the Fab City in Hyderabad. There is a possibility of something similar happening in Karnataka state as well.
Indeed, semiconductors are no longer business as usual! Right?
ASPs stabilizing, fab spend lower than expected
Future Horizons recently released the May WSTS results on the global semiconductor industry, which indicate that the chip market is slowly starting to buzz again. With the ‘hum back among the chips’, it was important for me to quiz Malcolm Penn, chairman and CEO, Future Horizons, in the UK, to find out why this was happening!
Now then, why is the chip market exactly humming? What has actually happened? Well, nothing specific! It is merely an overall step-by-step general improvement in everything, helped along by the normal seasonal improvement in business in the second half of the year!
So many forecasters and firms have their own forecasts. What happens now if some of these forecasts are cut or revised? Will that affect the market overall market? The answer is simple — a forecast is simply just that — a forecast — not fact!
Penn says, “The market will judge whether the other forecasters’ analyses of the market were right, as it wll indeed judge whether we are right too!”
Earlier, I had written about Future Horizons forecasting 12 percent growth in 2008 for the global semiconductor industry. Keep an eye on that one!
Further, have the ASPs stabilized, as those are indeed a dodgy lot? Penn feels, “We believe yes, although, there will still be the normal month-on-month variations and wobbles.”
Now, where does all of this leave the DRAM and NAND markets? According to the forecast, prices have already stopped falling as fast as they were this time last year.
However, they do fall and will fall; this is what they do! The question is: by how much? In other words, is the current fall above or below the long-term trend line? This will be analyzed in the long run as well.
Finally, what’s happening with the semicon equipment capex? Again, it is continuing to fall! “Right now we are in the middle of an underinvestment period, which means a capacity shortfall in 12 month’s time,” notes Penn.
No ‘fab’ times for fab spends
Is the fab spend going to see any change then? Well, unfortunately, no luck there! At least, not yet. Penn adds that fab spend is lower than expected at the beginning of the year.
He says: “The call then was for a 10 percent reduction, and this is now getting to be closer to 20 percent. In fact, Mike Splinter of Applied Materials is quoted as saying that he thinks that fab spend will end up 30 percent down.”
It is good to see that the global semiconductor industry is starting to hum a little bit more than what it was doing last month. Sincerely hope that the rest of the year pans out well!
Top 10 global semicon predictions — where are we today
 It is always interesting to write semicon blogs! Lots of people come up to me with their own comments, insights, requests, etc. One such request came from a friend in Taiwan, who’s involved with the semiconductor industry.
It is always interesting to write semicon blogs! Lots of people come up to me with their own comments, insights, requests, etc. One such request came from a friend in Taiwan, who’s involved with the semiconductor industry.
I was asked forthrightly what I thought of the top 10 global predictions, which I had blogged/written about some time back late last year.
Top 10 semicon predictions
For those who came in late, here are the 10 global predictions on semiconductors made at that time (late December 2007.
1. Semiconductor firms may have to face a recession year in an election year.
2. DRAM market looks weak in 2008.
3. NAND market will remain hot.
4. Power will remain a major issue.
5. EDA has to catch up.
6. Need to solve embedded (software crisis?) dilemma.
7. Consolidation in the fab space.
8. Capital equipment guys will continue to move to other market.
9. Spend on capital equipment to drop.
10. Mini fabs in developing countries.
Well, lot of water has flowed since those predictions were made. Let’s see how things stand, as of now. The updated predictions would look something like these:
1. There have been signs of recession, but the industry has faced it well, so far. In fact, Future Horizons feels that if there is going to be a global economic recession, the chip industry (but not all companies) is in the best shape possible to weather the ensuing storm.
2. Memory market is changing slightly as well, though people are very cautious. According to Converge, memory market prices appear to be stabilizing. iSuppli has predicted a poor year for DRAM though!
3. NAND Flash could show some recovery later this year. Yes, Q1-08 QoQ sales seems to have slipped, but the market remains hopeful of a recovery. Even iSuppli warned of NAND Flash slowdown in 2008, while Apple slashed its NAND order forecast significantly for 2008! Keep those fingers crossed!!
4. Power remains a big issue, and will continue to be so. This will remain as we move up newer technology process nodes.
5. EDA is seemingly catching up with 45nm designs. Magma, Synopsys, and the other leading EDA vendors are said to be playing big roles in 45nm designs.
6. Fabless companies are gaining in strength. No doubt about it! The 2007 semicon rankings show that. Also, Qualcomm is now the leader in the top wireless semicon suppliers, displacing Texas Instruments.
7. There have been consilidations (or long term alliances) in: a) fab space b) DRAM space. In the fab space, Intel, Samsung and TSMC have combined to go with 450mm wafer fab line by 2012. And in the DRAM space, there have been new camps, such as Elpida-Qimonda, and Nanya-Micron partnering to take on Samsung. With the global semiconductor market seeing steady decline in growth rate, which would continue, look forward to more consolidations.
8. Investments in photovoltaics (PV) have eased the pressure on capital equipment makers and spend somewhat. In fact, 2007 will be remembered as the year when the PV industry emerged as a key opportunity for subsystems suppliers and provided a timely boost in sales for those companies actively addressing this market. Perhaps, here lies an opportunity for India.
9. Mini fabs — these are yet to happen; so far talks only. In India, a single silicon wafer fab has yet to start functioning, even though it has been quite a while since the semicon policy was announced. Conversely, some feel that India should focus on design, rather than go after something as mature as having wafer fabs. However, several solar fabs — from Moser Baer, Videocon, Reliance, etc., are quite likely.
10. Moving to 45nm from 32nm is posing more design challenges than thought. This is largely due to the use of new materials. Well, 45nm will herald a totally different structure — metal gate/high-k/thin FET/deep trench design, etc. It will herald a new way of system design as well.
Now, I am not a semicon expert by any long distance, and welcome comments, suggestions, improvements from you all.
Top 20 global semicon companies — DRAM, Flash suppliers drop out
IC Insights recently published the May update to The McClean Report, featuring the Top 20 global semiconductor companies. Not surprisingly, there have been some significant movers and shakers. The most telling — quite a few of the major DRAM and Flash suppliers have dropped out of the Top 20 list!
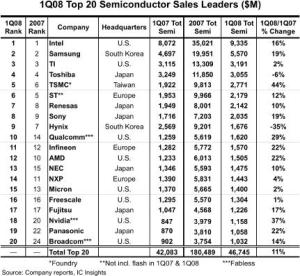 First the movers! Fabless supplier Qualcomm jumped up four spots, ranking as the 10th largest semiconductor supplier in Q1-08. Next, Broadcom, the third largest fabless supplier, also moved up four positions, up to the 20th position. Panasonic (earlier, Matsushita), moved up to the 19th position, while NEC of Japan moved up to the 13th position.
First the movers! Fabless supplier Qualcomm jumped up four spots, ranking as the 10th largest semiconductor supplier in Q1-08. Next, Broadcom, the third largest fabless supplier, also moved up four positions, up to the 20th position. Panasonic (earlier, Matsushita), moved up to the 19th position, while NEC of Japan moved up to the 13th position.
TSMC, the leading foundry, moved up one position, registering the highest — 44 percent — year-over-year Q1-08 growth rate, besides being ranked 5th. Nvidia, the second largest fabless supplier, was another company registering a high YoY growth rate of 37 percent, and moved into the 18th position. Some others like Infineon, Sony and Renesas also climbed a place higher each, respectively. The top four retained their positions — Intel, Samsung, TI and Toshiba.
And now, the shakers! The volatile DRAM and Flash markets have ensured the exit of several well known names such as Qimonda, Elpida, Spansion, Powerchip, Nanya, etc., from the list of the top 20 global semiconductor companies, at least for now.
Among the others in the list, the biggest drops were registered by NXP, which dropped to 14th from 11th last year, and AMD, which dropped two places, from 10th to 12th. Two memory suppliers — Hynix and Micron — also slipped two places, to 9th and 15th places, respectively. STMicroelectronics also slipped from 5th to 6th. IBM too slipped out of the top 20 list.
The top 20 global semiconductor firms comprises of eight US companies (including three fabless suppliers), six Japanese, three European, two South Korean, and one Taiwanese foundry (TSMC). Also, looking at the realities of the foundry market, TSMC’s lead is now unassailable. If TSMC was an IDM, it would be No. 2, challenging Intel and passing Samsung, said one analyst, recently, a thought shared by many.
IC Insights has reported that since the Euro and the Yen are strong against the dollar, this effect will impact global semiconductor market figures when reported in US dollars this year.
There are some other things to watch out for. Following a miserable 2007, the global DRAM module market is likely to rebound gradually in 2008 due to the projected recovery in the overall memory industry, according to an iSuppli report. That remains to be seen.
Some new DRAM camps — such as Elpida-Qimonda, and Micron-Nanya — have been formed. It will be interesting to see how these perform, as will be the performance of ST-backed Numonyx.
Further, the oversupply of NAND Flash worsened in Q1-08, impacted by the effect of the US sub-prime mortgage loan and a slow season, according to DRAMeXchange. The NAND Flash ASP fell about 35 percent compared to Q4-07. Although the overall bit shipment grew about 30 percent compared to Q4-07, the total Q1-08 sales of branded NAND Flash makers fell 15.8 percent QoQ to US$3.24bn. Will the NAND Flash market recover and by when?
NAND Q108 sales falls 15.8 percent
There’s a nice report today by DRAMeXchange on the state of the NAND Flash market. It is reproduced here.
Impacted by effect of the US sub-prime mortgage loan and a slow season, oversupply of NAND Flash worsened in 1Q08. NAND Flash ASP fell about 35 percent compared to 4Q07. Although the overall bit shipment grew about 30 percent compared to 4Q07, the total 1Q08 sales of branded NAND Flash makers fell 15.8 percent QoQ to US$3.24bn.
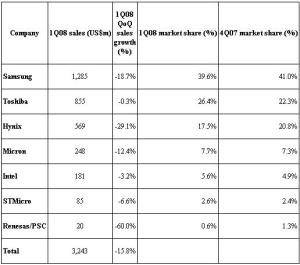 Ranked by the overall 1Q08 sales, Samsung continues to lead. The top five NAND Flash branded makers shared 96.8 percent of the whole market share in 1Q08.
Ranked by the overall 1Q08 sales, Samsung continues to lead. The top five NAND Flash branded makers shared 96.8 percent of the whole market share in 1Q08.
Although the NAND Flash market share by sales for Samsung in 1Q08 fell to roughly 39.6 percent compared to 4Q07, Samsung continues to be the leader in branded market.
Despite the increase proportion of 51nm node production, affected by the deep decline in NAND Flash price, 1Q08 sales fell 18.7 percent QoQ to US$1.28bn.
NAND Flash market share by sales for Toshiba rose to 26.4 percent compared to 4Q07 and continued to be in the second place among the branded NAND Flash makers.
Due to Toshiba’s successful increase in 56nm node production, it was able to resist the effect of the NAND Flash price decline. However, 1Q08 sales were flat compared to 4Q07 at US$855m.
The 1Q08 market share by sales for Hynix fell to 17.5 percent, though it continued to stay at the number three spot among branded NAND Flash makers. As Hynix lowered its NAND Flash production, 1Q08 bit shipment increased only 9 percent QoQ. However, due to the fall of NAND Flash ASP at 39 percent QoQ, 1Q08 sales for Hynix fell to US$569m, or a decline of 29.1 percent QoQ.
With the ramp up of 50nm node, Micron and Intel continued to see steady growth in a bit shipment in 1Q08. However, impacted by the large decline in NAND Flash price, their 1Q08 sales fell compared to 4Q07. Micron and Intel 1Q08 sales were US$248m and US$181m, respectively, with a market share of 7.7 percent and 5.6 percent, each.
As STMicroelectronics primarily produces NAND Flash for cell phone applications, revenue for 1Q08 was not as severely impacted by the price decline. Revenue for STMicro in 1Q08 fell slightly to US$85m, or a slight decline of 6.6 percent compared to 4Q07. The 1Q08 market share by sales was 2.6 percent.
Since Renesas continued to reduce its AG-AND Flash production in 1Q08, Renesas/PSC camp sales fell roughly 60 percent compared to 4Q07 with a market share of 0.6 percent.
New camps promise exciting times ahead in memory market
The last few weeks of this month witnessed some interesting developments in DRAM. No, there are not signs of a recovery, yet. Instead, the appearance of new DRAM camps, as well as a new memory interface working group, does generate some interest.
However, first, the stats. DRAMeXchange recently reported that the Q1-08 revenues of the branded DRAM makers, impacted by continual low DRAM prices, fell by roughly 5.8 percent compared to Q4-07. Likewise, the contract prices and the spot prices fell 19 percent and 11 percent respectively.
DRAMeXchange further reported that barring Elpida and Powerchip, all other DRAM makers experienced a decline in revenues. Both Elpida and Powerchip witnessed slight increase in their market share during Q1-08.
Categorizing the DRAM industry market share by countries, Japan only increased by 0.9 percent from 13.5 percent to 14.4 percent, as Elpida’s revenue increased in Q108. Taiwan’s share increased by only 1.1 percent from 13.6 percent to 14.7 percent, as Powerchip gained market share. Korea sustained the same market shares — 47.2 percent, as in Q4-07.
However, America and Germany lost share. America’s share slipped from 13.6 percent to 13 percent, while Germany’s share fell from 12.2 percent to 10.8 percent, respectively.
In a recent investor conference, Samsung announced it will increase its Bit Growth Rate from 70 percent to 100 percent, an indication of its desire to continue reigning as a DRAM market leader.
Now, to the really interesting developments. First, Nanya and Micron signed an agreement to create MeiYa Technology Corp., a new DRAM joint venture. One of Nanya’s 200mm facility in Taiwan will be upgraded to 300mm starting this year, with the facility going online for production in 2009. Besides MeiYa, Nanya and Micron will co-develop and share future technology.
If this wasn’t enough, close on the heels of the Micron-Nanya JV, Elpida Memory and Qimonda AG, signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for a technology partnership for jointly developing memory chips (DRAMs), and accelerate their roadmap to DRAM products featuring cell sizes of 4F2.
Analysts at DRAMeXchange believe that the Qimonda-Elpida alliance re-shuffles the DRAM competitive landscape. It is also a sign of Qimonda’s determination to develop stacked process.
Lastly, ARM, Hynix Semiconductor Inc., LG Electronics, Samsung Electronics, Silicon Image Inc., Sony Ericsson Mobile Communications AB, and STMicroelectronics announced the formation of a working group, the Serial Port Memory Technology (SPMT), which is committed to creating an open standard for next-generation memory interface technology targeting mobile devices.
SPMT, a first-of-its-kind memory standard for DRAM, is said to enable an extended battery life, bandwidth flexibility, significantly reduced pin count, lower power demand and multiple ports by using a serial interface instead of a parallel interface commonly used in today’s memory devices.
Handset vendors have joined the fray as this technology will not only extend battery life, it will allow high-performance media-rich applications as well, that are likely to be the norm on next-generation mobile phones.
Surely, these developments and the emergence of new camps promise some exciting times ahead in the memory market.
Top 10 global semiconductor trends for 2008
It is really difficult to stick your neck out and predict. That’s what makes the analyst’s jobs so difficult. Things happen and pass you by so quickly. For instance, as an example, who would have thought that Samsung would face a substantial blackout that would halt six chip production lines in a complex operated by the world’s largest flash memory producer?
Plans for the fab in India are now well under way. There have been questions like, do we need fabs? The year 2008 is the year of presidential elections and the Summer Olympics. Will we really see a recession in 2008? Here are some of the trends that are visible for 2008. Would love to hear from you.
1. Semiconductor firms may have to face a recession year in an election year
Yes, strange as it may sound, this just might happen! Concerns about consumer spending, caused by higher oil prices, mortgage crisis in the US and fears of a possible recession have made analysts more cautious, albeit optimistic. Analysts are wary of an impending recession in semiconductors during 2008. That, it should fall in the year of the US presidential elections makes it all the more intriguing. The nervousness is already showing in the slowing down of some markets.
2. DRAM market looks weak in 2008
Will DRAM prices rebound? Remains to be seen, although DRAMeXchange says that Taiwanese suppliers are likely to have their output to trim by 10-25 percent during February (Chinese New Year) as they usually plan for an average of 3-7 days of annual facility maintenance during this period. DRAMeXchange regards this as a possible catalyst for a price rebound in near term. Analysts haven’t helped either, with some saying DRAM will be on the slow side or even negative in H1-08.
3. NAND market will remain hot
You can bet, it will! Analysts remain upbeat for a positive NAND market in 2008. The reason being – new applications such as wireless USB, increase in cell phones memory capacities, higher content in portable media players, etc. We hope it is not a flash in the pan. There are rumors of another iPhone along the way!
4. Power will remain major issue
This isn’t going to change anytime soon! Power awareness is crucial for portable applications. It determines battery lifetime, and there’s an increased amount of computation involved as well. Power awareness is extremely crucial for high-performance applications. It determines cooling and energy costs. Many chip designs today are power limited and still require maximum performance.
5. EDA has to catch up
And fast! Analysts at a recent webcast hosted by Semiconductor International elaborated how the EDA industry was in a position of lag in the market. The DFM issue is increasingly becoming more complex. There is said to be a move to restrict the design rules that is in place now for 45nm. We are likely to see major changes in 32nm. That will have an impact on the EDA tools.
6. Need to solve the embedded dilemma
It is said that in 2007, the cost of designing or developing the embedded software for an SoC actually passed the cost of designing the SoC itself! We seem to be in the middle of a software crisis that is going to hit the entire electronics industry in the next five to six years.
Analysts are wary of an impending recession in semiconductors during 2008
7. Consolidation in the fab space
Some of the other older IDMs and fabs are said to be actually shutting down and going over to the foundries and process wafers for less than what they can do on their own. In this respect, we are seeing a lot of consolidation within the fab space. The mid-level players are consolidating. The customer base is clearly narrowing. The field is narrowing in 65nm and 45nm, and as we get to below 45nm, the field is going to get much, much narrower.
8. Capital equipment guys will continue to move to other markets
The best example, you can think of, is Applied Materials, which is into innovative equipment, service and software products for fabrication of chips, flat panel displays, solar photovoltaic cells, flexible electronics and energy efficient glass. Even the smaller guys are moving into LEDs or MEMS markets. That tells us what these companies are thinking about the semiconductors market.
9. Spend on capital equipment to drop
Gartner is expecting the long overdue capital spending correction in DRAM market to push the capital equipment market into contraction. Another slow year from foundry, along with concerns of US economic recession, adding to the downside. However, NAND spend should ramp up.
10. Mini fabs in developing countries
India has announced fab plans. There have also been talks of mega fabs and mini fabs elsewhere. There are going to be different types of fabs! With globalization, lot of countries may decide they want to have a fab. The market’s going to change.
However, bear in mind that the outlook on new fab starts appears weaker, as many companies have cut back on spending to wait for the market to improve. After a forecasted 8 percent YoY increase in fab construction spending in 2007, levels are likely to be flat in 2008.